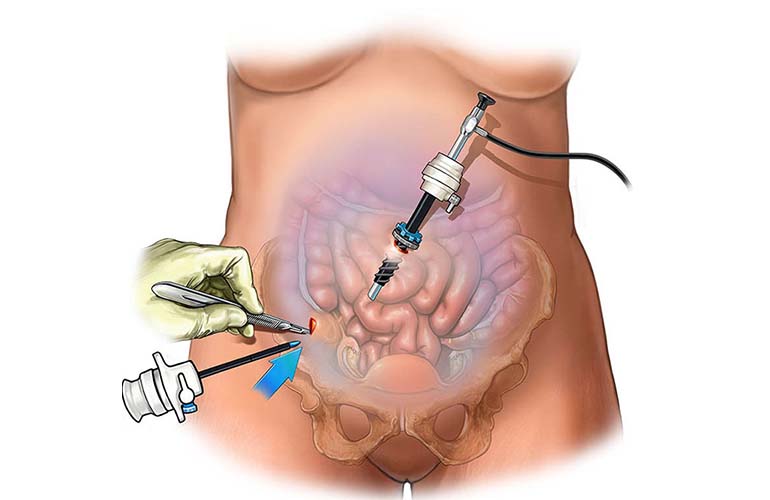
With the reflection of technological developments in medicine, laparoscopic procedures are also becoming increasingly common. Laparoscopy can generally be translated as observing the inside of the abdomen.
It is in the form of an intra-abdominal cavity, and the intra-abdominal organs are generally free, surrounded by a thin membrane. It is possible to monitor this cavity with special cameras by inflating it with a gas and to perform various surgeries with special hand tools.
Here, a few 0.5-1 cm incisions are made and pipe-like trocars are advanced into the abdomen and surgery is performed with the devices passed through here. Due to the small incisions, patients feel less pain after surgery and return to their daily lives much earlier.
The most frequently performed surgeries with this technique are gallbladder, appendix and hernia surgeries. Apart from this, bariatric surgery, reflux surgery, stomach, small and large intestine surgeries, spleen, liver, adrenal, kidney, uterus and ovary surgeries, even pancreatic surgeries that were obstructed at first, can be safely performed.

