What is an Abdominal Wall Hernia?
It is the ballooning of organs or tissues in the abdomen from a weak spot in the abdominal wall or through an anatomical opening that should normally be closed, together with the hernia sac, to the outside of the abdomen. It is one of the most common and treated diseases in surgical clinics.
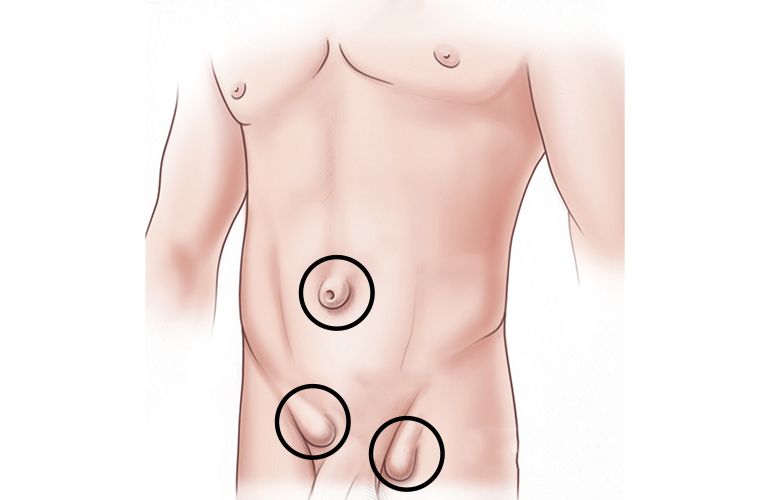
They take different names according to the region of the defect in the abdominal wall.
According to their location, abdominal wall hernias can be named as epigastric hernia between the navel and chest from top to bottom, umbilical hernia (umbilical hernia), periumbilical hernia around the umbilicus, inguinal hernia (inguinal hernia) in the inguinal areas, and femoral hernia. Special hernia types such as Spiegel hernia in the abdominal muscles and obturator hernia in the deep areas of the groin are rare. A type of hernia called incisional hernia (incisional hernia) may develop in any area where there is an incision due to weakness or opening in the abdominal wall after the operations.
Conditions such as chronic cough, difficulty urinating due to prostate disease, presence of intra-abdominal masses, chronic constipation, obesity, pregnancy are risk factors for the formation of abdominal wall hernias. Some connective tissue diseases also contribute to hernia formation.
The most common hernias are inguinal hernias. During the embryonic period, the testicles migrate to the bag called the scrotum. Meanwhile, the vessels feeding the testicles and the reproductive canal pass through an opening from the inside of the abdomen to the outside. This opening is normally closed. With advancing age and the above risk factors, this opening may widen or the inguinal wall may weaken and herniate outward. These are called inguinal (groin) hernias.
Femoral hernias are formed by the enlargement of the space next to the veins going to the leg.
The most important reason for the treatment of hernias is the suffocation of the hernia, which can be described as the compression of the contents and the deterioration of blood circulation. Apart from this, they may cause pain complaints, especially in the first periods.
Untreated hernias grow and deteriorate the patient's quality of life and aesthetic structure.
Treatment
Since there are real anatomical defects, the only treatment is surgical repair methods. Various types of patches can be used to provide tissue support during repair.
Hernia surgeries can be performed laparoscopically today. With this technique, it is possible to get rid of this disease with less incision and less pain. It should be considered as the ideal treatment option in experienced hands. The choice of open or laparoscopy in the treatment should be taken by the joint decision of the surgeon and the patient.
After the surgery, the patient is asked to comply with some protective measures such as not lifting heavy for a while, not doing heavy abdominal exercises. Relapses, albeit rare, may develop, especially in patients who do not comply with these precautions.

