Lesions that develop under the skin and under the skin, except for applications for aesthetic purposes, are included in the scope of general surgery.
These include large abscesses that develop as a result of various infective events that may develop on the skin, various tumors, benign and malignant tumors that develop under the skin and in the soft tissue up to the muscle.
Abscess on the skin, furuncle, carbuncle
When skin infections do not resolve spontaneously or with antibiotics, the infection may accumulate in one area and cause an abscess. The patient may have pain, redness, swelling and, in advanced cases, fever. There is a pus-like fluid inside the abscess cavity. A wall of connective tissue surrounds the abscess cavity, and unfortunately, antibiotics are less able to penetrate this wall or lose their activity due to the environment. For this reason, the main treatment of abscess is to drain and continue treatment with appropriate antibiotic.
The soft tissue inflammation called cellulitis in and around the abscess can sometimes become very large and turn into forms called carbuncles with the deterioration of the nutrition of the furuncle and abscess wall. These conditions severely impair the patient's quality of life. Their treatment is similar to the treatment of abscess, but since the infective space here will be very large, it may be necessary to wash this space intermittently.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (Dog Nipple)
It is a disease that progresses with many recurrent abscesses and flowing tunnels in some people, especially in the armpit and groin area. Although there is an abnormal infection of the glands in that area, problems related to the immune system are also blamed. In mild cases, oral and regional antibiotics, anti-inflammatories, various immune drugs are used in the treatment, while in advanced cases, surgical removal of the area as skin subcutaneous and closure of the opening is included. If the opening cannot be closed directly with the surrounding tissue, skin slides and skin patches can be used.
Skin tumors:
Until proven otherwise, moles that develop, grow, blister, crust, and bleed on the skin have the capacity to become a tumor. Particular attention should be paid to moles with irregular borders and more than one color.
Hard nodular lentil-like lesions of the skin, such as benign dermatofibroma, are treated by surgical removal, although they have a very low probability of developing a malignant character.
In the treatment of basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and malignant melanoma, which is a special type of skin cancer, it is essential to remove these tumors with clean surgical margins. If necessary, removal of the lymph nodes draining the tumor can be added to these procedures.
malignant melanoma; It is a malignant type of tumor of the skin. Its frequency increases with age. Some types are particularly directly related to exposure to sunlight. The incidence of the disease, which is defined by the presence of some individuals in the family or the presence of numerous and deteriorating moles in the body known as dysplastic nevus syndrome, increases. Diagnosis is made by examination, dermatoscopy and biopsy.
There are various types, mainly superficial spreading or nodular, which like to spread deeply. The most important factor determining survival is the depth reached by the tumor. Even if it is over 1 mm, it carries the tumor to Stage 2. Removal of the tumor with wide surgical margins is the gold standard in its treatment.
With lymph node marking, the first lymph node in which the lymph circulation of the tumor is emptied can be marked (sentinel lymph node sampling) and removed. Various non-surgical methods and chemotherapy may also provide partial benefit in patients who cannot be operated.
Subcutaneous and Soft Tissue Masses
Patients may apply to surgical clinics as a common complaint of various lumps and hardness of subcutaneous fat and connective tissue. Benign connective tissue tumors such as lipomas and fibromas constitute the majority of these masses. Locations can be different areas throughout the body.
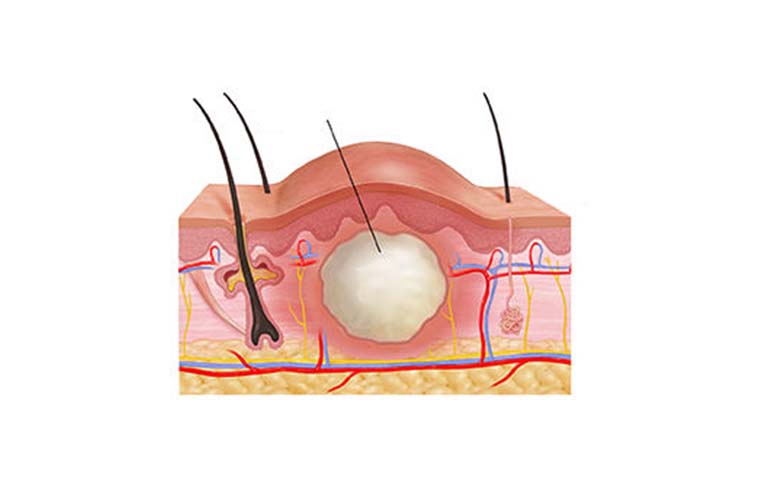
Sebaceous cysts may occur with the occlusion and cyst of the sebaceous glands in that area under the scalp. They appear as ball-like nodular lesions under the skin in varying sizes and numbers. Almost all of them are benign, they are treated by surgical removal, although there is a risk of recurrence from other areas.
Lipomas are the most common benign masses under the skin. They can reach sizes from a few millimeters to 20-25 cm. Diagnosis is made by examination and ultrasonography.
Complicated lesions that cannot be differentiated can be evaluated with MRI. As a general rule, lesions that are larger than 5 cm or that compress any vessel, nerve or tendon or cause pain should be removed. The patient's discomfort with this lesion is also a reason for removal.

